Mô tả bài toán
Tạo ứng dụng Console, khai báo các biến tương ứng với các kiểu dữ liệu có thể lưu trữ được thông tin cho:
Cách giải quyết
Xem source code Tham khảo để biết cách khai báo một số kiểu dữ liệu trong C#.
Ví dụ:
string hoTen = "Dương Nguyễn Phú Cường";
int gioiTinh = 0; //0: Nam; 1: Nữ; 2: Không công bố
string[] diaChi = new string[5]; // Mỗi người có 5 địa chỉ
diaChi[0] = "130 Xô Viết Nghệ Tỉnh, Quận Ninh Kiều, TP Cần Thơ";
diaChi[1] = "01 Lý Tự Trọng, Quận Ninh Kiều, TP Cần Thơ";
diaChi[2] = "";
diaChi[3] = "";
diaChi[4] = "";
DateTime ngaySinh = new DateTime(1989, 11, 06, 04, 00, 00);
Source code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DataTypeInCSharp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// https://learnxinyminutes.com/docs/csharp/
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Types & Variables
//
// Declare a variable using <type> <name>
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Sbyte - Signed 8-bit integer
// (-128 <= sbyte <= 127)
sbyte fooSbyte = 100;
// Byte - Unsigned 8-bit integer
// (0 <= byte <= 255)
byte fooByte = 100;
// Short - 16-bit integer
// Signed - (-32,768 <= short <= 32,767)
// Unsigned - (0 <= ushort <= 65,535)
short fooShort = 10000;
ushort fooUshort = 10000;
// Integer - 32-bit integer
int fooInt = 1; // (-2,147,483,648 <= int <= 2,147,483,647)
uint fooUint = 1; // (0 <= uint <= 4,294,967,295)
// Long - 64-bit integer
long fooLong = 100000L; // (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 <= long <= 9,223,372,036,854,775,807)
ulong fooUlong = 100000L; // (0 <= ulong <= 18,446,744,073,709,551,615)
// Numbers default to being int or uint depending on size.
// L is used to denote that this variable value is of type long or ulong
// Double - Double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 Floating Point
double fooDouble = 123.4; // Precision: 15-16 digits
// Float - Single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 Floating Point
float fooFloat = 234.5f; // Precision: 7 digits
// f is used to denote that this variable value is of type float
// Decimal - a 128-bits data type, with more precision than other floating-point types,
// suited for financial and monetary calculations
decimal fooDecimal = 150.3m;
// Boolean - true & false
bool fooBoolean = true; // or false
// Char - A single 16-bit Unicode character
char fooChar = 'A';
// Strings -- unlike the previous base types which are all value types,
// a string is a reference type. That is, you can set it to null
string fooString = "\"escape\" quotes and add \n (new lines) and \t (tabs)";
Console.WriteLine(fooString);
// You can access each character of the string with an indexer:
char charFromString = fooString[1]; // => 'e'
// Strings are immutable: you can't do fooString[1] = 'X';
// Compare strings with current culture, ignoring case
string.Compare(fooString, "x", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase);
// Formatting, based on sprintf
string fooFs = string.Format("Check Check, {0} {1}, {0} {1:0.0}", 1, 2);
// Dates & Formatting
DateTime fooDate = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine(fooDate.ToString("hh:mm, dd MMM yyyy"));
// Verbatim String
// You can use the @ symbol before a string literal to escape all characters in the string
string path = "C:\\Users\\User\\Desktop";
string verbatimPath = @"C:\Users\User\Desktop";
Console.WriteLine(path == verbatimPath); // => true
// You can split a string over two lines with the @ symbol. To escape " use ""
string bazString = @"Here's some stuff on a new line! ""Wow!"", the masses cried";
// Use const or read-only to make a variable immutable
// const values are calculated at compile time
const int HoursWorkPerWeek = 9001;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Data Structures
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Arrays - zero indexed
// The array size must be decided upon declaration
// The format for declaring an array is follows:
// <datatype>[] <var name> = new <datatype>[<array size>];
int[] intArray = new int[10];
// Another way to declare & initialize an array
int[] y = { 9000, 1000, 1337 };
// Indexing an array - Accessing an element
Console.WriteLine("intArray @ 0: " + intArray[0]);
// Arrays are mutable.
intArray[1] = 1;
// Lists
// Lists are used more frequently than arrays as they are more flexible
// The format for declaring a list is follows:
// List<datatype> <var name> = new List<datatype>();
List<int> intList = new List<int>();
List<string> stringList = new List<string>();
List<int> z = new List<int> { 9000, 1000, 1337 }; // initialize
// The <> are for generics - Check out the cool stuff section
// Lists don't default to a value;
// A value must be added before accessing the index
intList.Add(1);
Console.WriteLine("intList @ 0: " + intList[0]);
// Others data structures to check out:
// Stack/Queue
// Dictionary (an implementation of a hash map)
// HashSet
// Read-only Collections
// Tuple (.Net 4+)
//
// TODO: Khai báo các Biến dữ liệu cần thiết để có thể lưu trữ được Mẫu thông tin Lý lịch A2
// https://nentang.vn/khoa-hoc/dot-net/lap-trinh-can-ban-c-sharp/bai-hoc/khai-bao-cac-kieu-du-lieu-cho-mau-ly-lich-a2-va-mau-hoa-don-ban-hang/
//
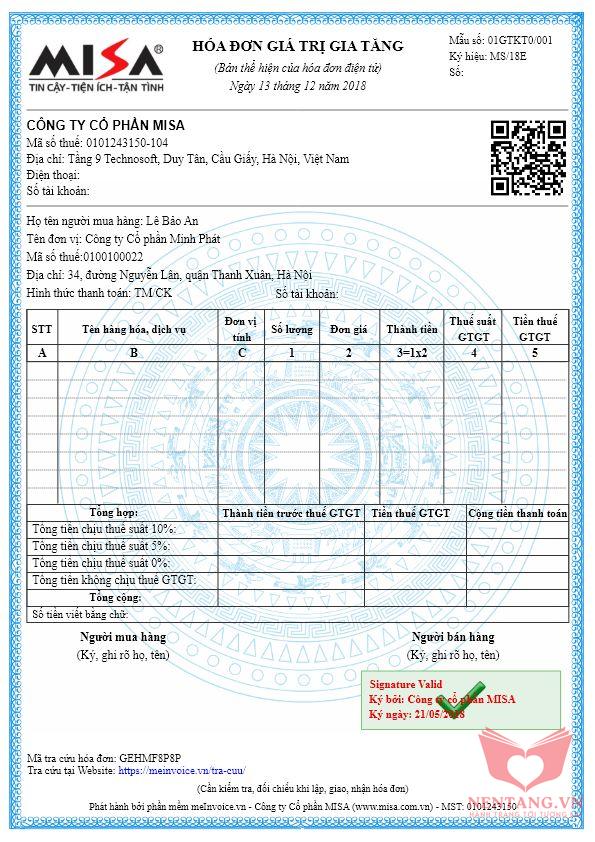
// TODO: Khai báo các Biến dữ liệu cần thiết để có thể lưu trữ được Mẫu hóa đơn bán hàng
// https://nentang.vn/khoa-hoc/dot-net/lap-trinh-can-ban-c-sharp/bai-hoc/khai-bao-cac-kieu-du-lieu-cho-mau-ly-lich-a2-va-mau-hoa-don-ban-hang/
}
}
}
Github
https://github.com/kellyfire611/learning.nentang.vn-csharp/tree/master/src/DataTypeInCSharp
|
