Đề bài
Cho mạng G có n đỉnh và m cạnh, đỉnh phát là 0, và đỉnh thu là n-1. Hãy tìm luồng f* trong mạng sao cho giá trị val(f*) của luồng f* là lớn nhất.
Input
- Dòng đầu tiên chứa 2 số n, m là số đỉnh và số cung trong mạng G.
- M dòng tiếp theo, mỗi dòng là 3 số u, v, c cho biết cung nối từ u đến v có trọng số là c.
Output
- Ghi một số nguyên dương cho biết giá trị luồng cực đại tìm được.
| Input |
Output |
| 6 9
1 2 10
1 3 10
2 3 2
2 4 4
2 5 8
3 5 9
4 6 10
5 4 6
5 6 10
|
19 |
Minh họa
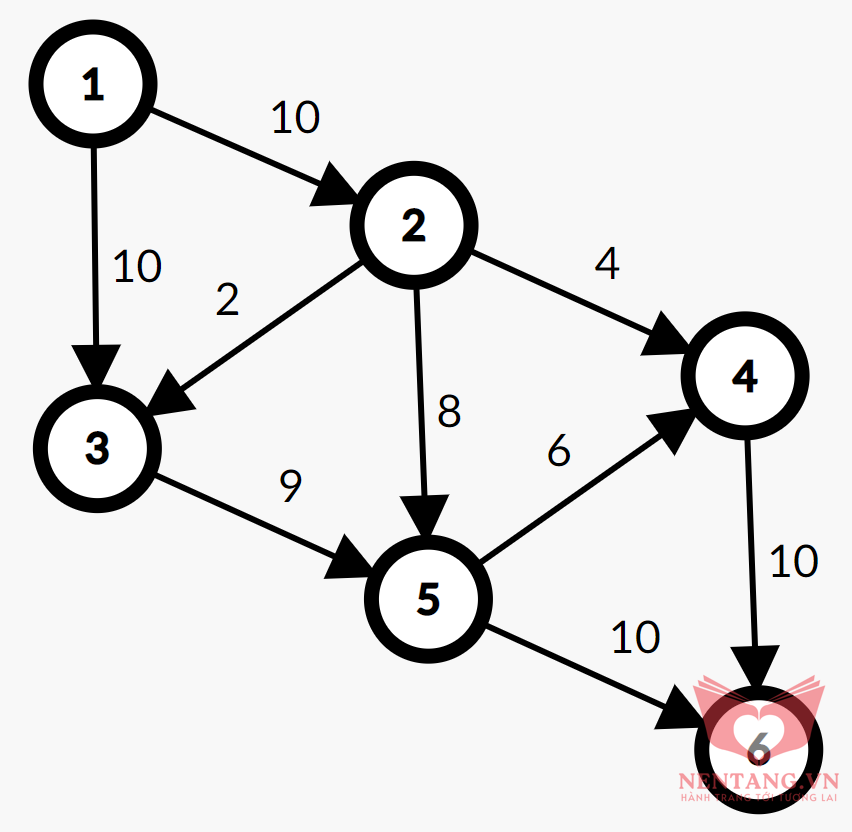
Giải
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int maxN = 1001;
const int INF = 1e9; // so vo cung
const int NULL_INT = -1;
int n, m; // n: so dinh, m: so canh
int s, t; // s: dinh bat dau, t: dinh ket thuc
vector<pair<int, int>> adj[maxN];
int parent[maxN];
int RC[maxN][maxN]; // luu tru cung xuoi, cung nguoc
int add_flow; // luu tru gia tri luong cuc dai
void inp() {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
adj[x].push_back({y, z});
// Do thi co huong thi comment dong code sau
adj[y].push_back({x, z});
// Luu tru gia tri trong so
RC[x][y] = z;
}
}
void dfs(int u) {
//cout << u << " ";
for(auto item: adj[u]) {
int v = item.first;
int w = item.second;
// Neu dinh v chua duoc tham
if(parent[v] == -1 && RC[u][v]) {
parent[v] = u; // Ghi nhan cha cua v la u
add_flow = min(add_flow, RC[u][v]);
dfs(v);
}
}
}
// Giai thuat Ford_Fulkerson
// s: dinh bat dau
// t: dinh ket thuc
// n: so luong dinh
int maxFlow_Ford_Fulkerson(int s, int t, int n) {
int flow = 0;
while(1) {
// Khoi tao
memset(parent, NULL_INT, sizeof(parent));
parent[s] = 0;
add_flow = INT_MAX;
dfs(s);
if(parent[t] == NULL_INT) {
break;
}
flow += add_flow;
int v = t;
while(v != s) {
int u = parent[v];
RC[v][u] += add_flow; // cung nguoc
RC[u][v] -= add_flow; // cung xuoi
v = u;
}
}
return flow;
}
int main() {
// Chuyen NHAP, XUAT thanh file
freopen("lab_8_input.INP", "r", stdin);
freopen("lab_8_output.OUT", "w", stdout);
// INPUT
inp();
// OUTPUT
int s = 1;
int t = n;
cout << maxFlow_Ford_Fulkerson(s, t, n);
return 0;
}
|