


Chương 4-Bài 1. Ngăn xếp - Stack
Tác giả: Dương Nguyễn Phú Cường
Số phút học: 107 phút
Số phút học: 107 phút
Ngày đăng:
12/3/2026, 16:25
Lượt xem: 1706
1. Lý thuyết về ngăn xếp(stack)
Trong khoa học máy tính, một ngăn xếp (còn gọi là bộ xếp chồng, tiếng Anh: Stack) là một cấu trúc dữ liệu trừu tượng hoạt động theo nguyên lý “vào sau ra trước” (Last In First Out (LIFO). Tức là, phần tử cuối cùng được chèn vào ngăn xếp sẽ là phần tử đầu tiên được lấy ra khỏi ngăn xếp. Một ví dụ trực quan, bạn có một chồng sách và bạn để nó trong một cái hộp như hình phía dưới. Giả sử hộp này vừa khít các cuốn sách. Khi đó, bạn có các thao tác:- Thêm một cuốn sách vào hộp(push của stack)
- Lấy một cuốn sách khỏi hộp, bạn chỉ lấy được thằng trên cùng(pop của stack)
- Push: Thêm một phần tử vào đỉnh của ngăn xếp, số phần tử của ngăn xếp tăng lên 1.
- Pop: Xóa bỏ phần tử đầu tiên ở đỉnh của ngăn xếp, số phần tử của ngăn xếp giảm đi 1.
- Top: Lấy giá trị của phần tử đầu tiên ở đỉnh của ngăn xếp, số phần tử của ngăn xếp không thay đổi.
- IsEmpty: Kiểm tra ngăn xếp trống hay không. Ngăn xếp trống là ngăn xếp không có phần tử nào.
- IsFull: Kiểm tra ngăn xếp đã đầy hay chưa. Thao tác này không phải lúc nào cũng có.
- Size: Lấy số lượng phần tử stack đang có.
2. Cài đặt ngăn xếp bằng mảng
Tại mục hướng dẫn này, mình sẽ cùng các bạn đi chi tiết từng thao tác của cấu trúc dữ liệu ngăn xếp. Chúng ta sẽ triển khai cài đặt ngăn xếp các số nguyên sử dụng mảng. Ở mục tiếp theo, tôi sẽ cung cấp cho các bạn một số cách cài đặt khác nữa. Chúng ta sẽ sử dụng mảng 1 chiều kiểu int làm Stackstack, một biến capacity để lưu kích thước(sức chứa) của stack và một biến top để lưu chỉ số của phần tử ở top của Stack stack.
2.1. Kiểm tra stack đầy(IsFull)
Hàm này sẽ kiểm tra xemstack hiện tại đã đầy hay chưa. Nếu chỉ số top của stack đang bằng với capacity - 1, tức stack đã đầy.
bool IsFull(int capacity){
if(top >= capacity - 1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
2.2. Kiểm tra stack rỗng(IsEmpty)
Nếu như stack đang không có phần tử nào, ta sẽ gán chỉ số top = -1 để đánh dấu. Như vậy, để kiểm tra stack có đang rỗng hay không rất đơn giản. Ta chỉ cần so sánh giá trị top có phải -1 hay không mà thôi.bool IsEmpty(){
if(top == -1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
2.3. Thêm phần tử vào đỉnh stack(Push)
Chúng ta sẽ chỉ có thể push(thêm phần tử) vào đỉnh stack khi stack chưa đầy. Nếu stack đầy, chúng ta sẽ đưa ra thông báo và không thực hiện push. Ngược lại, ta sẽ tăng top lên một đơn vị và gán giá trị cho phần tử tại chỉ số top.void Push(int stack[], int value, int capacity){
if(IsFull(capacity) == true){
printf("\nStack is full. Overflow condition!");
}else{
++top;
stack[top] = value;
}
}
2.4. Xóa phần tử khỏi đỉnh stack(Pop)
Chúng ta sẽ chỉ có thể pop(xóa phần tử) khỏi đỉnh stack khi stack không trống. Nếu stack trống, chúng ta sẽ đưa ra thông báo và không thực hiện pop. Ngược lại, ta sẽ giảm giá trị top đi một đơn vị.void Pop(){
if(IsEmpty() == true){
printf("\nStack is empty. Underflow condition!");
}else{
--top;
}
}
2.5. Lấy giá trị phần tử ở đỉnh stack(Top)
Để lấy giá trị phần tử ở đỉnh stack, ta có thao tác rất đơn giản:int Top(int stack[]){
return stack[top];
}
2.6. Lấy số lượng phần tử stack đang có(Size)
Biếntop lưu chỉ số lớn nhất của stack. Như vậy, việc lấy size của stack cực kỳ đơn giản:
int Size(){
return top + 1;
}
Và cuối cùng, chúng ta sẽ có 1 chương trình cài đặt stack hoàn thiện như sau:
#include <stdio.h>
int top = -1;
bool IsFull(int capacity){
if(top >= capacity - 1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
bool IsEmpty(){
if(top == -1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
void Push(int stack[], int value, int capacity){
if(IsFull(capacity) == true){
printf("\nStack is full. Overflow condition!");
}else{
++top;
stack[top] = value;
}
}
void Pop(){
if(IsEmpty() == true){
printf("\nStack is empty. Underflow condition!");
}else{
--top;
}
}
int Top(int stack[]){
return stack[top];
}
int Size(){
return top + 1;
}
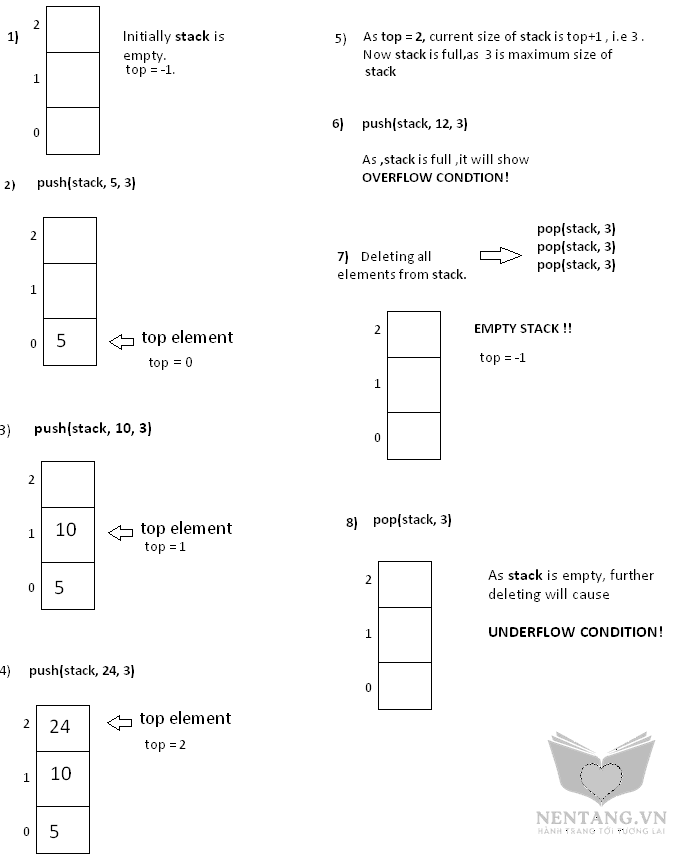
int main(){
int capacity = 3;
int top = -1;
int stack[capacity];
// pushing element 5 in the stack .
Push(stack, 5, capacity);
printf("\nCurrent size of stack is %d", Size());
Push(stack, 10, capacity);
Push(stack, 24, capacity);
printf("\nCurrent size of stack is %d", Size());
// As the stack is full, further pushing will show an overflow condition.
Push(stack, 12, capacity);
//Accessing the top element
printf("\nThe current top element in stack is %d", Top(stack));
//Removing all the elements from the stack
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3;i++)
Pop();
printf("\nCurrent size of stack is %d", Size());
//As the stack is empty , further popping will show an underflow condition.
Pop();
}
Kết quả chạy chương trình trên:
Current size of stack is 1 Current size of stack is 3 Stack is full. Overflow condition! The current top element in stack is 24 Current size of stack is 0 Stack is empty. Underflow condition!
3. Ứng dụng của stack
Chúng ta sẽ sử dụng stack vào bài toán kiểm tra dãy ngoặc có hợp lệ hay không. Bạn có một dãy các dấu ngoặc bao gồm ngoặc đóng ‘)’ và ngoặc mở ‘(‘. Bạn phải kiểm tra xem dãy ngoặc đó có hợp lệ hay không. Một dãy ngoặc hợp lệ thì sẽ không thừa dấu ngoặc hoặc không có dấu ngoặc lẻ loi, chẳng hạn như: (), (()), ((()))() là các dãy ngoặc hợp lệ. Còn ((, ()), (()( là các dãy ngoặc không hợp lệ. Bạn có thể giải quyết bài toán này với stack. Hãy xem chúng ta làm như thế nào nhé. Ý tưởng: Duyệt qua từng dấu ngoặc trong dãy ngoặc; Sử dụng một stack để push các dấu ngoặc mở vào stack, mỗi khi gặp dấu ngoặc đóng, thực hiện pop một phần tử khỏi stack. Dãy ngoặc sẽ không hợp lệ khi bạn không thể pop hoặc khi kết thúc duyệt mà stack vẫn chưa rỗng.#include <stdio.h>
int top;
void check (char str[ ], int n, char stack [ ])
{
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++ )
{
if (str [ i ] == '(')
{
top = top + 1;
stack[ top ] = '(';
}
if(str[ i ] == ')' )
{
if(top == -1 )
{
top = top -1 ;
break ;
}
else
{
top = top -1 ;
}
}
}
if(top == -1)
printf("String is balanced!\n");
else
printf("String is unbalanced!\n");
}
int main ( )
{
//balanced parenthesis string.
char str[ ] = "(())()";
// unbalanced string .
char str1 [] = "((()";
char stack [15] ;
top = -1;
check (str , 9 , stack ); //Passing balanced string
top = -1 ;
check(str1 , 5 , stack) ; //Passing unbalanced string
return 0;
}
Kết quả
String is balanced! String is unbalanced!
4. Một số cách cài đặt ngăn xếp khác
4.1. Cài đặt stack động bằng mảng
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<limits.h>
typedef struct Stack
{
int top;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
}Stack;
Stack* createStack(unsigned capacity)
{
struct Stack* stack = (Stack*) malloc(sizeof(Stack));
stack->capacity = capacity;
stack->top = -1;
stack->array = (int*) malloc(stack->capacity * sizeof(int));
return stack;
}
int Full(Stack* stack)
{ return stack->top == stack->capacity - 1; }
int Empty(Stack* stack)
{ return stack->top == -1; }
void push(Stack* stack, int item)
{
if (Full(stack))
return;
stack->array[++stack->top] = item;
printf("%d pushed to stack\n", item);
}
int pop(Stack* stack)
{
if (Empty(stack))
return INT_MIN;
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
int peek(Stack* stack)
{
if (Empty(stack))
return INT_MIN;
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
int main()
{
Stack* stack = createStack(100);
push(stack, 14);
push(stack, 25);
push(stack, 38);
push(stack, 48);
printf("%d popped from stack\n", pop(stack));
printf("Top item is %d\n", peek(stack));
return 0;
}
//output
/*14 pushed to stack
25 pushed to stack
38 pushed to stack
48 pushed to stack
48 popped from stack
Top item is 38*/
4.2. Cài đặt stack sử dụng hướng đối tượng C++
#define Maxsize 10
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class stacks
{
public:
int Top=-1;
int s[10];
void push(int);
void pop();
void print();
};
void stacks::push(int x)
{
if(Top==Maxsize)
{
cout<<"Error : cannot insert";
}
else
{
Top++;
s[Top]=x;
}
}
void stacks::pop()
{
if(Top<0)
{
cout<<"Error : cannot delete";
}
else
{
Top--;
return;
}
}
void stacks::print()
{
int i;
cout<<"Stack:";
for(i=Top;i>=0;i--)
{
cout<<s[i];
}
}
int main()
{
stacks o;
int e,i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cin>>e;
o.push(e);
}
//o.pop();
o.print();
}
4.3. Cài đặt stack sử dụng danh sách liên kết
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Stack
{
int data;
Stack *next;
} *TOS = NULL;
void Push(int value)
{
Stack *new_node = new Stack();
new_node -> data = value;
new_node -> next = TOS;
TOS = new_node;
}
void Pop()
{
if(TOS == NULL)
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl;
else
{
Stack *temp;
temp = TOS;
TOS = TOS -> next;
temp -> next = NULL;
delete temp;
}
}
void Print_Stack()
{
if(TOS == NULL)
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl;
else
{
cout << "Top of stack is " << TOS -> data << endl;
if(TOS -> next != NULL)
{
cout << "Other Elements are : ";
Stack *current = TOS -> next;
while(current)
{
cout << current -> data << " ";
current = current -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
Push(i);
Print_Stack();
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
Pop();
Print_Stack();
return 0;
}
/* Output
Top of stack is 4
Other Elements are : 3 2 1 0
Stack is empty
Stack is empty
*/
4.4. Sử dụng stack trong thư viện STL
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
int main () {
std::stack<int> mystack;
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i) mystack.push(i);
std::cout << "Popping out elements...";
while (!mystack.empty()) {
std::cout << ' ' << mystack.top();
mystack.pop();
}
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
5. Bài tập thực hành
Cho một biểu thức hậu tố với số hạng là các số nguyên dương và ba toán tử +, -, *. Hãy tính giá trị của biểu thức hậu tố. Ví dụ: biểu thức hậu tố: 2 3 4 + * 5 – 2 2 * + có giá trị là 13. Dữ liệu nhập: – Gồm một dòng thể hiện biểu thức hậu tố, mỗi số hạng là một số nguyên dương trong phạm vi từ 1 đến 100. Giữa hai số hạng, hoặc giữa hai toán tử, hoặc giữa số hạng và toán tử, cách nhau một khoảng trắng. Chiều dài biểu thức không quá 100 ký tự. Dữ liệu đề bài cho đảm bảo biểu thức hậu tố là hợp lệ. Trong quá trình tính toán đảm bảo trị tuyệt đối các giá trị trung gian không vượt quá 109. Dữ liệu xuất: – Là giá trị của biểu thức hậu tố. Lưu ý: dùng hàm gets() hay getline() để đọc chuỗi. Ví dụ
#input:
2 3 4 + * 5 - 2 2 * +
#output:
13
Bình luận
Bình luận của bạnNền tảng các kiến thức học tập
Cùng nhau học tập, khám phá các kiến thức nền tảng về Lập trình web, mobile, database nhé.
Nền tảng kiến thức - Hành trang tới tương lai hân hạnh phục vụ Quý khách!
Khám phá, trải nghiệm ngay

Vui lòng đăng nhập để gởi bình luận!
Đăng nhậpChưa có bình luận nào!