


Chương 3-Bài 9. Bắt các lỗi/ngoại lệ (Exception) trong C#
Số phút học: 76 phút
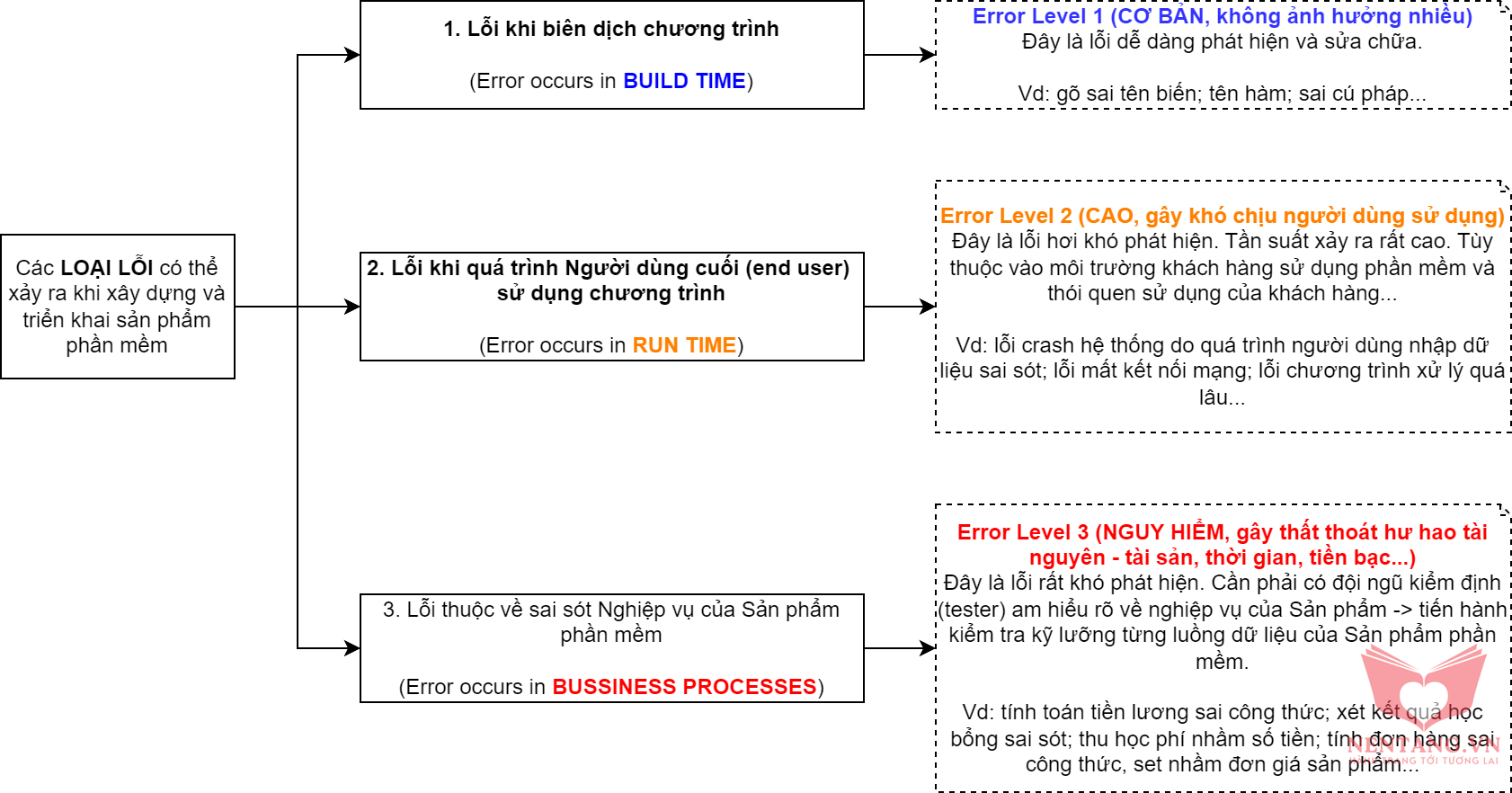
Các loại lỗi có thể xảy ra khi xây dựng và triển khai sản phẩm phần mềm
An exception is a problem that arises during the execution of a program. A C# exception is a response to an exceptional circumstance that arises while a program is running, such as an attempt to divide by zero.
Exceptions provide a way to transfer control from one part of a program to another. C# exception handling is built upon four keywords: try, catch, finally, and throw.
- try − A try block identifies a block of code for which particular exceptions is activated. It is followed by one or more catch blocks.
- catch − A program catches an exception with an exception handler at the place in a program where you want to handle the problem. The catch keyword indicates the catching of an exception.
- finally − The finally block is used to execute a given set of statements, whether an exception is thrown or not thrown. For example, if you open a file, it must be closed whether an exception is raised or not.
- throw − A program throws an exception when a problem shows up. This is done using a throw keyword.
Syntax
Assuming a block raises an exception, a method catches an exception using a combination of the try and catch keywords. A try/catch block is placed around the code that might generate an exception. Code within a try/catch block is referred to as protected code, and the syntax for using try/catch looks like the following −
try {
// statements causing exception
} catch( ExceptionName e1 ) {
// error handling code
} catch( ExceptionName e2 ) {
// error handling code
} catch( ExceptionName eN ) {
// error handling code
} finally {
// statements to be executed
}
You can list down multiple catch statements to catch different type of exceptions in case your try block raises more than one exception in different situations.
Exception Classes in C#
C# exceptions are represented by classes. The exception classes in C# are mainly directly or indirectly derived from the System.Exception class. Some of the exception classes derived from the System.Exception class are the System.ApplicationException and System.SystemException classes.
The System.ApplicationException class supports exceptions generated by application programs. Hence the exceptions defined by the programmers should derive from this class.
The System.SystemException class is the base class for all predefined system exception.
The following table provides some of the predefined exception classes derived from the Sytem.SystemException class −
| Sr.No. | Exception Class & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
System.IO.IOException Handles I/O errors. |
| 2 |
System.IndexOutOfRangeException Handles errors generated when a method refers to an array index out of range. |
| 3 |
System.ArrayTypeMismatchException Handles errors generated when type is mismatched with the array type. |
| 4 |
System.NullReferenceException Handles errors generated from referencing a null object. |
| 5 |
System.DivideByZeroException Handles errors generated from dividing a dividend with zero. |
| 6 |
System.InvalidCastException Handles errors generated during typecasting. |
| 7 |
System.OutOfMemoryException Handles errors generated from insufficient free memory. |
| 8 |
System.StackOverflowException Handles errors generated from stack overflow. |
Handling Exceptions
C# provides a structured solution to the exception handling in the form of try and catch blocks. Using these blocks the core program statements are separated from the error-handling statements.
These error handling blocks are implemented using the try, catch, and finally keywords. Following is an example of throwing an exception when dividing by zero condition occurs −
using System;
namespace ErrorHandlingApplication {
class DivNumbers {
int result;
DivNumbers() {
result = 0;
}
public void division(int num1, int num2) {
try {
result = num1 / num2;
} catch (DivideByZeroException e) {
Console.WriteLine("Exception caught: {0}", e);
} finally {
Console.WriteLine("Result: {0}", result);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
DivNumbers d = new DivNumbers();
d.division(25, 0);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Exception caught: System.DivideByZeroException: Attempted to divide by zero. at ... Result: 0
Creating User-Defined Exceptions
You can also define your own exception. User-defined exception classes are derived from the Exception class. The following example demonstrates this −
using System;
namespace UserDefinedException {
class TestTemperature {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Temperature temp = new Temperature();
try {
temp.showTemp();
} catch(TempIsZeroException e) {
Console.WriteLine("TempIsZeroException: {0}", e.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
public class TempIsZeroException: Exception {
public TempIsZeroException(string message): base(message) {
}
}
public class Temperature {
int temperature = 0;
public void showTemp() {
if(temperature == 0) {
throw (new TempIsZeroException("Zero Temperature found"));
} else {
Console.WriteLine("Temperature: {0}", temperature);
}
}
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
TempIsZeroException: Zero Temperature found
Throwing Objects
You can throw an object if it is either directly or indirectly derived from the System.Exception class. You can use a throw statement in the catch block to throw the present object as −
catch(Exception e) {
...
Throw e
}
Bình luận
Bình luận của bạnNền tảng các kiến thức học tập
Cùng nhau học tập, khám phá các kiến thức nền tảng về Lập trình web, mobile, database nhé.
Nền tảng kiến thức - Hành trang tới tương lai hân hạnh phục vụ Quý khách!
Khám phá, trải nghiệm ngay

Vui lòng đăng nhập để gởi bình luận!
Đăng nhậpChưa có bình luận nào!