


Chương 2-Bài 9. Điều kiện trong C#
Tác giả: Dương Nguyễn Phú Cường
Số phút học: 76 phút
Số phút học: 76 phút
Ngày đăng:
27/2/2026, 0:31
Lượt xem: 1523
Decision making structures requires the programmer to specify one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be true, and optionally, other statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be false.
Following is the general form of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages −
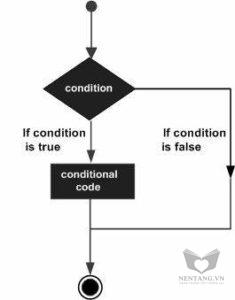 C# provides following types of decision making statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
C# provides following types of decision making statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
 C# provides following types of decision making statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
C# provides following types of decision making statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
| Sr.No. | Statement & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. |
| 2 | An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is false. |
| 3 | You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else ifstatement(s). |
| 4 | A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. |
| 5 | You can use one switch statement inside another switchstatement(s). |
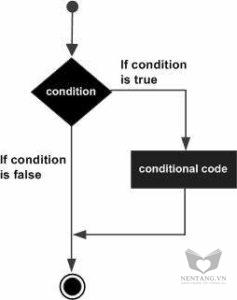
If statement
An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements.Syntax
The syntax of an if statement in C# is −if(boolean_expression) {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */
}
If the boolean expression evaluates to true, then the block of code inside the if statement is executed. If boolean expression evaluates to false, then the first set of code after the end of the if statement(after the closing curly brace) is executed.
Flow Diagram

Example
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
/* local variable definition */
int a = 10;
/* check the boolean condition using if statement */
if (a < 20) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
Console.WriteLine("a is less than 20");
}
Console.WriteLine("value of a is : {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
a is less than 20; value of a is : 10
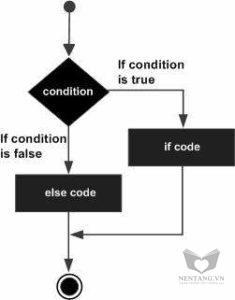
If...else statement
An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is false.Syntax
The syntax of an if...else statement in C# is −if(boolean_expression) {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */
} else {
/* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false */
}
If the boolean expression evaluates to true, then the if block of code is executed, otherwise else block of code is executed.
Flow Diagram

Example
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
/* check the boolean condition */
if (a < 20) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
Console.WriteLine("a is less than 20");
} else {
/* if condition is false then print the following */
Console.WriteLine("a is not less than 20");
}
Console.WriteLine("value of a is : {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
a is not less than 20; value of a is : 100
The if...else if...else Statement
An if statement can be followed by an optional else if...else statement, which is very useful to test various conditions using single if...else if statement. When using if, else if, else statements there are few points to keep in mind.- An if can have zero or one else's and it must come after any else if's.
- An if can have zero to many else if's and they must come before the else.
- Once an else if succeeds, none of the remaining else if's or else's will be tested.
Syntax
The syntax of an if...else if...else statement in C# is −if(boolean_expression 1) {
/* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 2) {
/* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 3) {
/* Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true */
} else {
/* executes when the none of the above condition is true */
}
Example
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
/* local variable definition */
int a = 100;
/* check the boolean condition */
if (a == 10) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 10");
}
else if (a == 20) {
/* if else if condition is true */
Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 20");
}
else if (a == 30) {
/* if else if condition is true */
Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 30");
} else {
/* if none of the conditions is true */
Console.WriteLine("None of the values is matching");
}
Console.WriteLine("Exact value of a is: {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
None of the values is matching Exact value of a is: 100
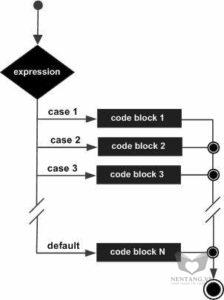
Switch
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being switched on is checked for each switch case.Syntax
The syntax for a switch statement in C# is as follows −switch(expression) {
case constant-expression1 :
statement(s);
break;
case constant-expression2 :
case constant-expression3 :
statement(s);
break;
/* you can have any number of case statements */
default : /* Optional */
statement(s);
}
The following rules apply to a switch statement −
- The expression used in a switch statement must have an integral or enumerated type, or be of a class type in which the class has a single conversion function to an integral or enumerated type.
- You can have any number of case statements within a switch. Each case is followed by the value to be compared to and a colon.
- The constant-expression for a case must be the same data type as the variable in the switch, and it must be a constant or a literal.
- When the variable being switched on is equal to a case, the statements following that case will execute until a break statement is reached.
- When a break statement is reached, the switch terminates, and the flow of control jumps to the next line following the switch statement.
- Not every case needs to contain a break. If no break appears, then it will raise a compile time error.
- A switch statement can have an optional default case, which must appear at the end of the switch. The default case can be used for performing a task when none of the cases is true.
Flow Diagram

Example
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
/* local variable definition */
char grade = 'B';
switch (grade) {
case 'A':
Console.WriteLine("Excellent!");
break;
case 'B':
case 'C':
Console.WriteLine("Well done");
break;
case 'D':
Console.WriteLine("You passed");
break;
case 'F':
Console.WriteLine("Better try again");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Invalid grade");
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("Your grade is {0}", grade);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Well done Your grade is B
The ? : Operator
We have covered conditional operator ? : in previous chapter which can be used to replace if...else statements. It has the following general form −Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;Where Exp1, Exp2, and Exp3 are expressions. Notice the use and placement of the colon. The value of a ? expression is determined as follows: Exp1 is evaluated. If it is true, then Exp2 is evaluated and becomes the value of the entire ? expression. If Exp1 is false, then Exp3 is evaluated and its value becomes the value of the expression.
Bình luận
Bình luận của bạnNền tảng các kiến thức học tập
Cùng nhau học tập, khám phá các kiến thức nền tảng về Lập trình web, mobile, database nhé.
Nền tảng kiến thức - Hành trang tới tương lai hân hạnh phục vụ Quý khách!
Khám phá, trải nghiệm ngay

Vui lòng đăng nhập để gởi bình luận!
Đăng nhậpChưa có bình luận nào!