


Chương 5-Bài 1. Khai báo các Kiểu dữ liệu cho Mẫu Lý lịch A2 và Mẫu Hóa đơn Bán hàng
Tác giả: Dương Nguyễn Phú Cường
Số phút học: 111 phút
Số phút học: 111 phút
Ngày đăng:
1/3/2026, 11:19
Lượt xem: 1874
Mô tả bài toán
Tạo ứng dụng Console, khai báo các biến tương ứng với các kiểu dữ liệu có thể lưu trữ được thông tin cho:- Mẫu Lý lịch Công chức A2
- Mẫu Hóa đơn Bán hàng
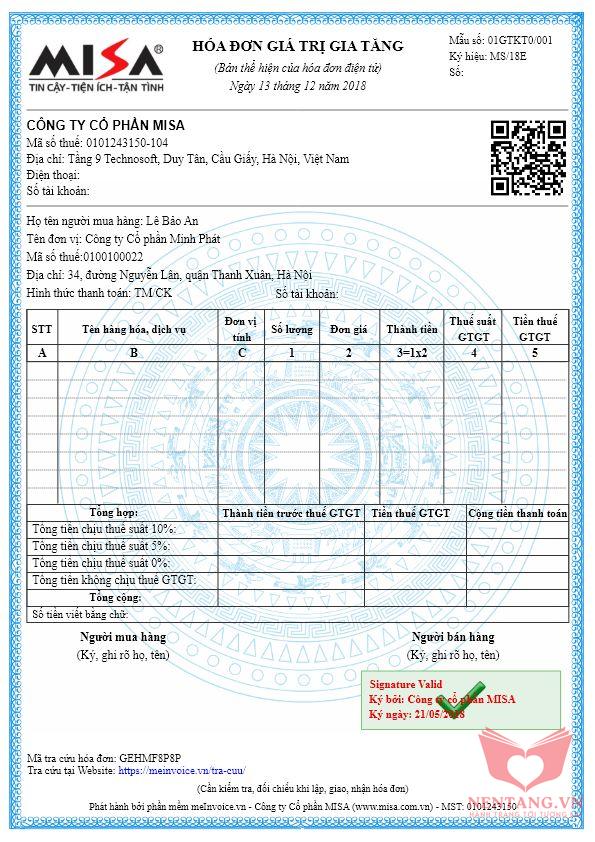
Cách giải quyết
Xem source code Tham khảo để biết cách khai báo một số kiểu dữ liệu trong C#. Ví dụ:string hoTen = "Dương Nguyễn Phú Cường"; int gioiTinh = 0; //0: Nam; 1: Nữ; 2: Không công bố string[] diaChi = new string[5]; // Mỗi người có 5 địa chỉ diaChi[0] = "130 Xô Viết Nghệ Tỉnh, Quận Ninh Kiều, TP Cần Thơ"; diaChi[1] = "01 Lý Tự Trọng, Quận Ninh Kiều, TP Cần Thơ"; diaChi[2] = ""; diaChi[3] = ""; diaChi[4] = ""; DateTime ngaySinh = new DateTime(1989, 11, 06, 04, 00, 00);
Source code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace DataTypeInCSharp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// https://learnxinyminutes.com/docs/csharp/
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Types & Variables
//
// Declare a variable using <type> <name>
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Sbyte - Signed 8-bit integer
// (-128 <= sbyte <= 127)
sbyte fooSbyte = 100;
// Byte - Unsigned 8-bit integer
// (0 <= byte <= 255)
byte fooByte = 100;
// Short - 16-bit integer
// Signed - (-32,768 <= short <= 32,767)
// Unsigned - (0 <= ushort <= 65,535)
short fooShort = 10000;
ushort fooUshort = 10000;
// Integer - 32-bit integer
int fooInt = 1; // (-2,147,483,648 <= int <= 2,147,483,647)
uint fooUint = 1; // (0 <= uint <= 4,294,967,295)
// Long - 64-bit integer
long fooLong = 100000L; // (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 <= long <= 9,223,372,036,854,775,807)
ulong fooUlong = 100000L; // (0 <= ulong <= 18,446,744,073,709,551,615)
// Numbers default to being int or uint depending on size.
// L is used to denote that this variable value is of type long or ulong
// Double - Double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 Floating Point
double fooDouble = 123.4; // Precision: 15-16 digits
// Float - Single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 Floating Point
float fooFloat = 234.5f; // Precision: 7 digits
// f is used to denote that this variable value is of type float
// Decimal - a 128-bits data type, with more precision than other floating-point types,
// suited for financial and monetary calculations
decimal fooDecimal = 150.3m;
// Boolean - true & false
bool fooBoolean = true; // or false
// Char - A single 16-bit Unicode character
char fooChar = 'A';
// Strings -- unlike the previous base types which are all value types,
// a string is a reference type. That is, you can set it to null
string fooString = "\"escape\" quotes and add \n (new lines) and \t (tabs)";
Console.WriteLine(fooString);
// You can access each character of the string with an indexer:
char charFromString = fooString[1]; // => 'e'
// Strings are immutable: you can't do fooString[1] = 'X';
// Compare strings with current culture, ignoring case
string.Compare(fooString, "x", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase);
// Formatting, based on sprintf
string fooFs = string.Format("Check Check, {0} {1}, {0} {1:0.0}", 1, 2);
// Dates & Formatting
DateTime fooDate = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine(fooDate.ToString("hh:mm, dd MMM yyyy"));
// Verbatim String
// You can use the @ symbol before a string literal to escape all characters in the string
string path = "C:\\Users\\User\\Desktop";
string verbatimPath = @"C:\Users\User\Desktop";
Console.WriteLine(path == verbatimPath); // => true
// You can split a string over two lines with the @ symbol. To escape " use ""
string bazString = @"Here's some stuff on a new line! ""Wow!"", the masses cried";
// Use const or read-only to make a variable immutable
// const values are calculated at compile time
const int HoursWorkPerWeek = 9001;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Data Structures
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Arrays - zero indexed
// The array size must be decided upon declaration
// The format for declaring an array is follows:
// <datatype>[] <var name> = new <datatype>[<array size>];
int[] intArray = new int[10];
// Another way to declare & initialize an array
int[] y = { 9000, 1000, 1337 };
// Indexing an array - Accessing an element
Console.WriteLine("intArray @ 0: " + intArray[0]);
// Arrays are mutable.
intArray[1] = 1;
// Lists
// Lists are used more frequently than arrays as they are more flexible
// The format for declaring a list is follows:
// List<datatype> <var name> = new List<datatype>();
List<int> intList = new List<int>();
List<string> stringList = new List<string>();
List<int> z = new List<int> { 9000, 1000, 1337 }; // initialize
// The <> are for generics - Check out the cool stuff section
// Lists don't default to a value;
// A value must be added before accessing the index
intList.Add(1);
Console.WriteLine("intList @ 0: " + intList[0]);
// Others data structures to check out:
// Stack/Queue
// Dictionary (an implementation of a hash map)
// HashSet
// Read-only Collections
// Tuple (.Net 4+)
//
// TODO: Khai báo các Biến dữ liệu cần thiết để có thể lưu trữ được Mẫu thông tin Lý lịch A2
// https://nentang.vn/khoa-hoc/dot-net/lap-trinh-can-ban-c-sharp/bai-hoc/khai-bao-cac-kieu-du-lieu-cho-mau-ly-lich-a2-va-mau-hoa-don-ban-hang/
//
// TODO: Khai báo các Biến dữ liệu cần thiết để có thể lưu trữ được Mẫu hóa đơn bán hàng
// https://nentang.vn/khoa-hoc/dot-net/lap-trinh-can-ban-c-sharp/bai-hoc/khai-bao-cac-kieu-du-lieu-cho-mau-ly-lich-a2-va-mau-hoa-don-ban-hang/
}
}
}
Github
https://github.com/kellyfire611/learning.nentang.vn-csharp/tree/master/src/DataTypeInCSharpBình luận
Bình luận của bạnNền tảng các kiến thức học tập
Cùng nhau học tập, khám phá các kiến thức nền tảng về Lập trình web, mobile, database nhé.
Nền tảng kiến thức - Hành trang tới tương lai hân hạnh phục vụ Quý khách!
Khám phá, trải nghiệm ngay

Vui lòng đăng nhập để gởi bình luận!
Đăng nhậpChưa có bình luận nào!